Ink Settings
The ink settings are required for separation profiles and DotProof profiles. For ContoneProof profiles, the ink settings are not relevant.
You can define the ink settings for characterizations and projects. In a project, under the Proof tab, you can define the ink settings of all colors used in the project. Under the Separation tab, you can define only the actual output colors as defined by the Target Color Space.
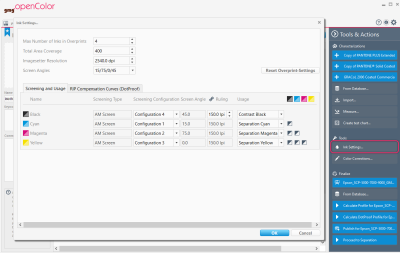
On characterization and project level, you can access the ink settings via the Tools & Actions panel on the right: Tools & Actions > Tools > Ink Settings
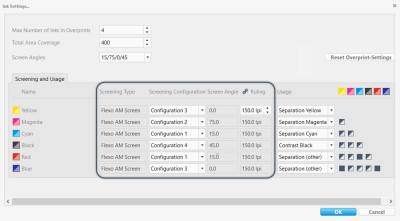
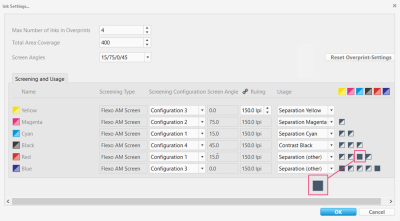
Screening
This screenshot highlights the Screening area of the ink settings.
The Screening settings are mandatory for calculating DotProof and separation profiles. Including the imagesetter resolution, the screening settings should match the actual target printing conditions you want to simulate, e.g. as used for creating the 1-bit files of the iteration chart (see "Optimizing the Profile Quality").
Different screening grids serve to avoid moiré patterns. If you want to print with more than four inks, you can use the same grid for complementary colors, as complementary colors normally do not overprint. For example, Red can have the same grid as Cyan, and Green the same as Magenta. If the colors strongly differ in lightness, however, they should use different screening grids.
The screen angles of the separate channels should be shifted at least by 15° towards each other for avoiding moiré effects. Instead of defining each angle separately, you can use one of the typical presets (> Screen Configuration).
If the screening settings used when producing the 1-bit files differ from the ones in the characterization (e.g. when using 1-Bit Creator in GMG ColorProof), the first ones should be used.
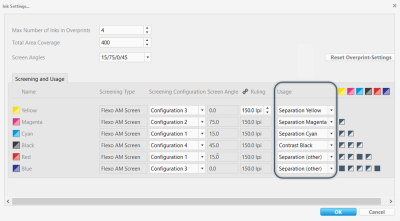
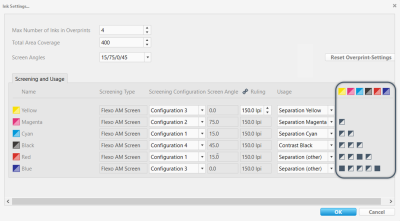
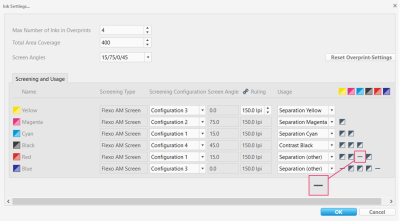
Usage
This screenshot highlights the Usage area of the ink settings.
The Usage setting defines how a color will be handled during profile calculation. It also influences the choice of patches and the total number of patches in iteration test charts used for DotProof profiling.
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
| Separation
(Cyan, Magenta, Yellow, other) |
Select this option for image separations and important colors (including spot colors) that need to be reproduced in a detailed way. Inks that are defined as separations are profiled with all overprint information available in the characterization. When calculating a separation profile, all output inks need to be defined as Separation except Contrast (Black). |
| Contrast (Black) | Use this option for shadow-enhancing colors such as black. |
| Spot Color | Select this option for colors that are used only as typical spots and are not part of the image separation. |
| Solid Only | Use this option for all colors that are used only as full tone. |
| Color Database | GMG OpenColor will use this Usage type if you are adding a whole spot color library to a project as an 'ink'. You can do this if you are using a project to dynamically generate proof profiles from a fixed set of colors plus colors from a spot color library, for example, CMYK + a spot color library. |
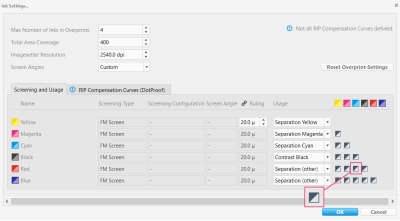
Overprint
This screenshot highlights the Overprint matrix of the ink settings.
The overprint behavior depends on the Screening and Usage settings.
In case of AM screening, colors set to the same screening configuration will overprint only with solids by default. For example, if Cyan and Red are both set to Configuration 1, Cyan will only print with solid Red and vice versa. In the overprint matrix, this is indicated by the filled Suppress Raster-Raster overprints icon (
With the 
You can click the icons in the overprint matrix to change the overprint behavior. For example, you could prevent Cyan and Red from overprinting by setting them to Suppress all Overprints (
With the 
In case of FM screening, there are no predefined screening configurations available. Instead, you can define the overprint behavior for each color individually and without limits via the overprint matrix. For example, you could allow overprinting for all colors by setting each of them to All overprints, no restrictions (
With the 
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
 Suppress all overprints Suppress all overprints |
This option ensures that excluded colors do not overprint at all and helps to avoid color shifts caused by register deviations in conventional printing, particularly in Flexo. However, if excluded colors do not overprint at all, this may lead to very steep curves and small breaks at transitions between non-overprinting colors. |
|
|
This is the default setting. It is particularly beneficial for digital printing machines with accurate registration and can also be applied in Offset printing. Excluded colors generally do not overprint, but there will be slight overlaps to allow smoother transitions. These intentional overlaps, typically just a few percentage points, usually do not result in visible color shifts in case of register differences. |
 All overprints, no restrictions All overprints, no restrictions |
When printing with more than four colors, this setting is only available for FM screening. Colors are allowed to overprint without limitations, ensuring smooth transitions and gradients and achieving the maximum possible gamut. Colors are mixed only when it makes sense in terms of color space, though. |
When calculating separation rules, the Total Area Coverage and the overprint behavior defined in the project are taken into account (see "Creating Color Definitions"). This prevents overinking and moiré effects in the print production.